Welding is a fundamental process in various industries, allowing metals to be joined securely. One crucial element of welding is the use of filler wires—consumable materials that enhance the strength and quality of welds. This guide explores six essential types of welding filler wires for both TIG and laser welding.
What Is Welding Filler Wire?
A welding filler wire is a consumable metal rod used to bridge the gap between two metal workpieces during the welding process. It melts and fuses with the base metals, forming a strong, consistent bond. Filler wires are essential for achieving high-quality welds, enhancing strength, corrosion resistance, and durability.
In TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, the filler wire is manually fed into the weld pool, while in laser welding, the focused laser beam melts the filler wire precisely. Choosing the right filler wire depends on the type of metal, welding technique, and desired weld characteristics.
Types of Welding Filler Wire
Welding filler wires come in various types, each suited for specific applications. Choosing the right filler wire depends on the base metal, welding method, and desired weld quality. Below are the six most common types of welding filler wires you need to know.
1. Mild Steel Filler Wire (e.g., ER70S-6)
Mild steel filler wire is used for welding low-carbon steel. It has high iron content with traces of carbon, silicon, and manganese. This type is suitable for both TIG and laser welding. Mild steel filler wire is widely used in automotive manufacturing, general fabrication, and sheet metal welding. It produces clean, smooth welds with good strength.
2. Stainless Steel Filler Wire (e.g., ER308L, ER309L)
Stainless steel filler wire contains nickel and chromium, offering excellent corrosion resistance. It is used for welding stainless steel in both TIG and laser welding applications. This wire is ideal for chemical tanks, food-grade equipment, and structural projects. Stainless steel filler wire provides strong, durable welds with a clean, polished finish.
3. Aluminum Filler Wire (e.g., ER4045, ER5356)
Aluminum filler wire is designed for welding aluminum and aluminum alloys. It is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and offers excellent electrical conductivity. Aluminum filler wire is used in TIG and laser welding, suitable for automotive, aerospace, and marine applications. It produces clean, smooth welds but requires precise control to avoid overheating.
4. Nickel Alloy Filler Wire
Nickel alloy filler wire is known for its heat and corrosion resistance. It is used in welding high-temperature alloys in industries like aerospace, petrochemical and nuclear. Both TIG and laser welding can use nickel alloy filler wire. It delivers strong, durable welds that withstand extreme conditions.
5. Bronze and Copper-Based Filler Wire
Bronze and copper-based filler wires are used for welding copper, brass, and bronze. They offer excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. These wires are commonly applied in electrical equipment manufacturing, plumbing and art metalwork. They are suitable for TIG and laser welding, resulting in strong, smooth joints.
6. Titanium and Specialty Alloy Filler Wires
Titanium filler wires are lightweight and corrosion-resistant. They are used in aerospace, medical equipment and chemical processing industries. These wires are compatible with both TIG and laser welding. Titanium filler wire produces strong, precise welds, making it suitable for high-performance applications. Specialty alloy filler wires, such as those made from cobalt or other metals, are also available for specific welding needs.
How to Choose the Right Filler Wire for Laser Welding
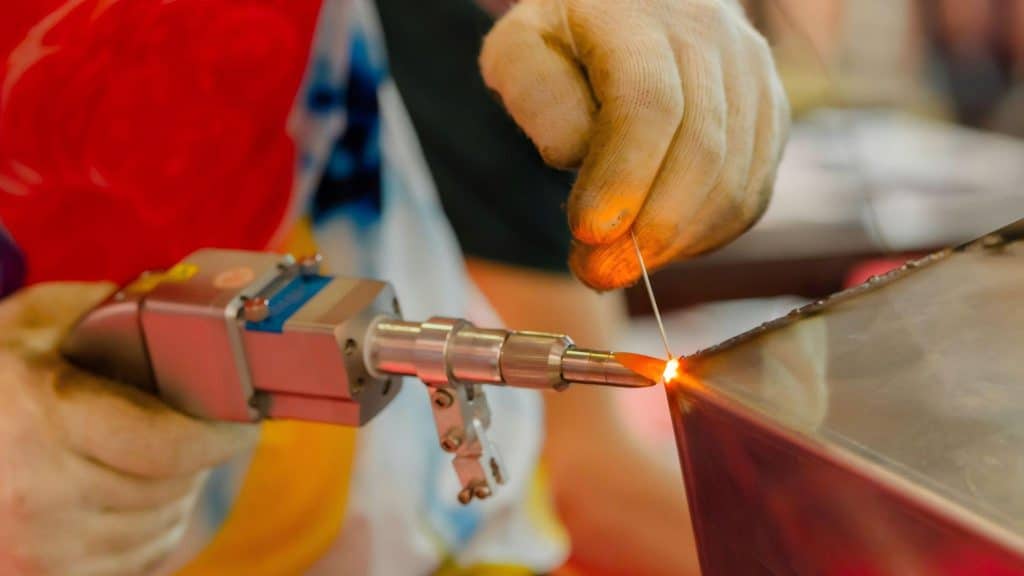

Selecting the appropriate filler wire for laser welding is vital for achieving strong, precise joints. The filler wire must closely match the base metal’s composition to prevent defects and corrosion. For instance, use ER70S-6 for mild steel and ER4043 or ER5356 for aluminum alloys. These choices ensure compatibility and optimal weld quality.
Wire diameter influences the weld pool’s stability. Thinner wires melt faster, suitable for delicate tasks, while thicker wires are better for heavy-duty applications. Adjust laser parameters—power, speed and focus—according to the wire type and material thickness to maintain control over the weld.
Shielding gas, typically argon or a mix with helium, protects the weld from oxidation. Ensure the gas flow rate is adequate to cover the weld area without turbulence.
For enhanced performance, consider using advanced equipment like the DenaliWeld Jet 1000. This portable laser welding machine features a patented CUAL mosaic laser source, offering consistent output and precision. Its modular design simplifies maintenance, and the integrated automatic wire feeder ensures smooth wire delivery. The Jet 1000’s user-friendly interface and compact size make it ideal for various applications, from automotive repairs to intricate metalwork.
By carefully selecting the filler wire and utilizing advanced tools, you can achieve high-quality, reliable laser welds.
Achieve Precision Welding with DenaliWeld
Welding filler wires are essential for achieving strong, precise welds in both TIG and laser welding. Understanding the types of filler wires and choosing the right one for your project can significantly improve weld quality. For advanced laser welding solutions, explore DenaliWeld’s premium products. Visit DenaliWeld’s Product Page to find the perfect welding equipment.



