Introduction
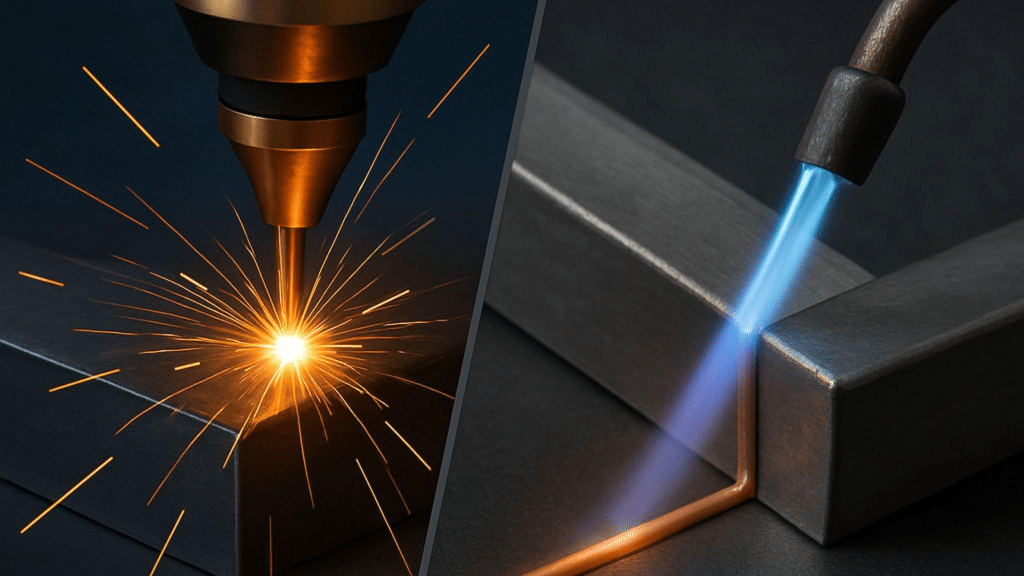
Many manufacturers often rely on brazing to fuse metal surfaces. It is an old-school yet versatile technique that produces clean joints. However, many see brazing as unreliable in terms of weld strength and consistency.
On one hand, laser welding is considered the most efficient and fastest welding method today. It creates strong welds quickly with minimal thermal distortion.
So, is laser welding better than brazing? Read on as we compare laser welding vs brazing in this article and see which one would fare better in modern production processes.
Laser Welding vs. Brazing: The Basics
Laser welding pertains to the use of a highly concentrated laser beam to melt a workpiece’s surface and join it to another piece upon cooling. This technique is well-known for its pinpoint precision as it melts localized spots with minimal heat-affected zones.
Meanwhile, brazing joins the metal workpieces without fusing their surfaces. Instead, it creates a metallurgical bond through a filler metal (also known as the brazing alloy) brought into contact with the heated workpieces. Brazing is widely used in joining metals with different melting points.
How Does Laser Welding Work?

In laser welding, an external energy source such as a flashlamp, electric current, or another laser excites particles along a medium to generate a coherent beam of light. When this focused light beam strikes the material, it quickly heats and penetrates a small area on its surface, forming a molten pool. The materials are then joined as the pool cools.
The effectiveness of this process highly depends on the machine’s quality. A high-precision, portable, and efficient machine such as Denaliweld’s Air-Cooled Laser Welding Machine can produce strong and defect-free welds. This lightweight, 90-pound laser welding machine comes with easily adjustable, one-click operation controls and a user-friendly modular structure for optimal performance even in extreme environments, ranging from -10°C to 40°C (14°F to 104°F).
How Does Brazing Work?
Brazing works through capillary action, the phenomenon by which liquid flows through a narrow channel even without external forces. The filler material like bronze, silver, or brass is liquefied by intense heat. Then, it is drawn into the joint of the base metals. Through capillary action, the molten filler material flows into the narrow gaps between the metals and fills the joint.
Unlike in welding, brazing melts only the filler material and not the conjoining metals. Capillary action cannot occur in welding because of the absence of a solid surface where the molten filler material can flow through.
Which One Creates a Stronger Weld: Laser Welding vs Brazing?
Both techniques ensure adequate weld strength for various applications, but laser-welded joints are considerably stronger and longer-lasting than brazing joints.
When the materials are molten in laser welding, they are fused at a molecular level which results in stronger metallurgical bonds. And since this method does not rely on a filler material, the joint adopts almost completely the strength and durability of the parent materials.
Moreover, since laser welding creates joints with minimal heat-affected zones, distortion on the parent materials is also minimized. This means that laser-welded joints are less prone to cracking and corrosion.
Which is More Efficient? Speed, Cost, and Energy Usage Compared
The accuracy and controlled heat input in laser welding makes it faster compared to brazing. It can penetrate metals up to 40 to 400 inches per minute, which is highly beneficial when penetrating thin and delicate materials to prevent overheating.
Laser welding also has a lower setup time compared to brazing. The latter requires meticulous heating of the base and filler materials at a certain temperature level, which requires some time to accomplish. Meanwhile, you can strike the beam from the laser welding machine right away and melt the materials almost instantly.
Between the two, laser welding is also more energy-efficient because its high-powered beam precisely strikes the weld area without wasting energy. Its concentrated energy requires less overall heat to melt a material, which translates to efficient energy usage. On one hand, brazing must meet the filler material’s specific melting point which may result in longer heat application and energy consumption.
Price-wise, brazing requires less initial investment than laser welding. This is because laser welding requires a sophisticated and high-priced machine for optimal performance. However, laser welding’s high-speed performance means higher joint volume but reduced production time, which drives down operating costs even in the long run. And since laser-welded joints are stronger and cleaner than brazing joints, this means that laser welding can save you time and resources from post-welding remedies.
Common Applications: Where to Use Laser Welding vs. Brazing
Laser welding creates stronger welds that can resist stress and corrosion over time. So, it is the ideal method for industries that require high-strength, durable, and reliable joints to ensure people’s safety and product integrity.
- Automotive: For heavy-duty joints in vehicle frames, panels, and engines.
- Aerospace: For the production of lightweight, durable bonds in turbines, engines, and hydraulic systems.
- Medical devices: For the production of contaminant-free and reliable surgical equipment and diagnostic tools.
- Electronics: For precise integration of small, thin, and delicate electronic components such as microchips and semiconductors.
Meanwhile, brazing remains a good choice for applications by which aesthetics or versatility is prioritized more than strength and durability. It is reliable in the jewelry, plumbing, and HVAC industry.
Is Laser Welding or Brazing Best for You?
Both methods can achieve high-quality welds. But the better approach between the two depends on certain factors.
Strength requirements: Laser-welded joints are generally stronger and more durable compared to brazing joints. They also adopt the parent material’s strength better because of their non-reliance on a filler material.
Material compatibility: Both methods are versatile and work well with similar or dissimilar metals. However, laser welding’s ultra-speed and precision make it a better choice for penetrating thin materials without overheating.
Precision needs: The focused beam of laser welding makes it highly precise in targeting specific areas with minimal thermal distortion and heat-affected zone.
Cost and efficiency: Brazing requires a lower initial investment than laser welding, but laser welding drives down overall operating costs in the long run. Laser welding is also more efficient because it can penetrate, melt, and fuse metals faster than brazing.
Laser Welding vs. Brazing: The Choice is Now Yours
Considering precision, weld strength, speed, cost, and energy efficiency, we have a clear winner-laser welding. Of course, brazing is still a reliable method for creating clean and strong welds, but laser welding fares better with its longer-lasting and durable joints that can withstand extreme conditions and stress.
It is time to make a choice. If you are considering adopting laser welding for your business operations, go to Denaliweld for our range of laser welding solutions which are all CE and SSG-certified. We are committed to delivering high laser welding performance with our products made by industry professionals, and with your satisfaction in mind. Choose Denaliweld today.



